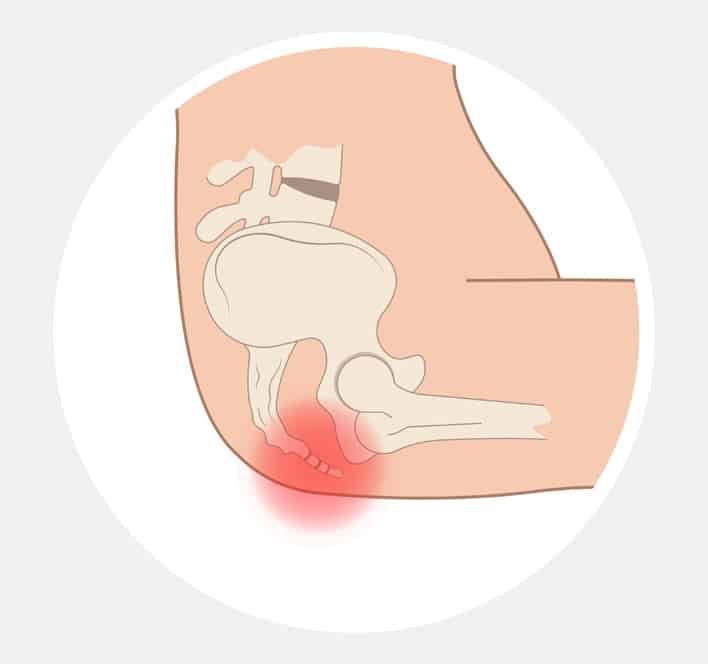
The surgical removal of the coccyx (tailbone) is known as coccygectomy. It is recommended when other treatments, such as steroid injections and physiotherapy, have failed to relieve tailbone pain. Although considered rare, a surgical removal of the tailbone, which forms the base of the spine, is often the last resort for patients who do not respond to any non-surgical interventions.
Many patients report positive outcomes in terms of pain relief when seasoned orthopedic or spinal surgeons perform a partial or complete coccygectomy. If you’ve experienced unexplained lower back pain, NJ Spine & Orthopedic and our team of highly-trained doctors and patient advocates can help you get the care you deserve.
Signs of a Damaged Coccyx
While tailbone fractures are relatively uncommon, direct trauma or injury is the most likely cause of a broken tailbone. A damaged tailbone in a young adult can be caused by a backward fall or a high-impact accident. Broken coccyxes are more common in older people due to nutritional deficiencies. Pain and tenderness at the base of the spine are the most common symptoms of coccyx damage.
The area may feel dull and achy, with occasional sharp pains that intensify when you bend forward, sit down, or stand up. Additional symptoms of tailbone damage include:
- Tingling or numbness in the legs
- Pain and straining during bowel movement
- A visible bruise in the tailbone area if the injury was due to trauma
- The tailbone area experiences severe localized pain and tenderness
- Pain is exacerbated by direct pressure to the tailbone area, such as with prolonged sitting
If you believe you have a damaged coccyx, meet with your doctor to see if you would benefit from a coccygectomy.
Who Can Benefit From a Coccygectomy?
The coccyx is a small, triangular, tail-like bone near the anus comprising three to five smaller bones. A direct impact on the coccyx can damage or break the tailbone. Such an injury commonly happens during contact sports or in a physical fight. A coccyx injury can also occur due to a car collision or a slip-and-fall accident.
In some cases, when a woman gives birth, her coccyx may break. A person may also start experiencing coccyx pain without knowing why, which could necessitate the removal of some or all of their tailbones. A coccygectomy is performed to alleviate symptoms like pain and tenderness. You may be a candidate for a coccygectomy if you have persistent pain in your coccyx area due to any of the following reasons:
- The discomfort is because of congenital defects
- You have fractures caused by dislocations and high-impact trauma
- The tailbone has been damaged as a result of aging or a degenerative disease
- An infection has occurred or spread throughout the sacral and coccyx
- A rare type of tumor called sacrococcygeal teratoma (SCT) (commonly diagnosed in newborns) is growing in the tailbone area
Before considering a coccygectomy, patients with tailbone issues are encouraged to try non-surgical approaches. Surgical interventions are considered if the pain doesn’t resolve in a few months.
What Happens During a Coccygectomy?
A medical history and a physical exam may help determine the cause of a coccyx injury. To examine the entire spine, a neurologic exam may be done. A rectal exam may also be performed to determine whether there is a dislocation or coccyx fracture and if direct pressure on the tailbone induces pain. While an X-ray may not always reveal specific injuries, it may be used to rule out a fracture or dislocation.
Whenever non-surgical treatment does not relieve persistent pain, a coccygectomy is considered. Surgeons take different approaches to the procedure depending on the patient’s diagnosis. Some opt to remove a portion of the coccyx, while others take out the entire tailbone. An orthopedic or spinal surgeon will perform a coccygectomy under general anesthesia. This procedure generally entails:
- A surgeon making a one to two-inch incision over the top of the coccyx, directly under the skin and subcutaneous fat tissue
- Dissecting what’s known as the periosteum (protective cartilage over the bone) from the bone and lifting it around the front
- Extracting the coccyx. If the surgeon suspects a tumor, it’s subjected to a biopsy
The surgical treatment takes about 30 minutes and can be done as an outpatient procedure. This operation has a lengthy recovery period and makes sitting challenging throughout the healing process. Nonetheless, patients typically experience relief from their symptoms three months to a year after surgery.
Hire a Spinal Surgeon from NJ Spine and Orthopedic Today
A broken tailbone is a rare yet painful injury that can affect anyone at any age. At NJ Spine & Orthopedic, we focus on pain management and preventing further tailbone trauma. A coccygectomy, or tailbone removal, aids in the removal of a dislocated, unstable, or broken coccyx following an accidental injury.
If you’re experiencing chronic tailbone pain and have tried a spectrum of non-surgical treatments but failed, consider the potential benefits of a coccygectomy. Call us at (866) 553-0612 or complete our online contact form to schedule a comprehensive appointment for your spinal condition.